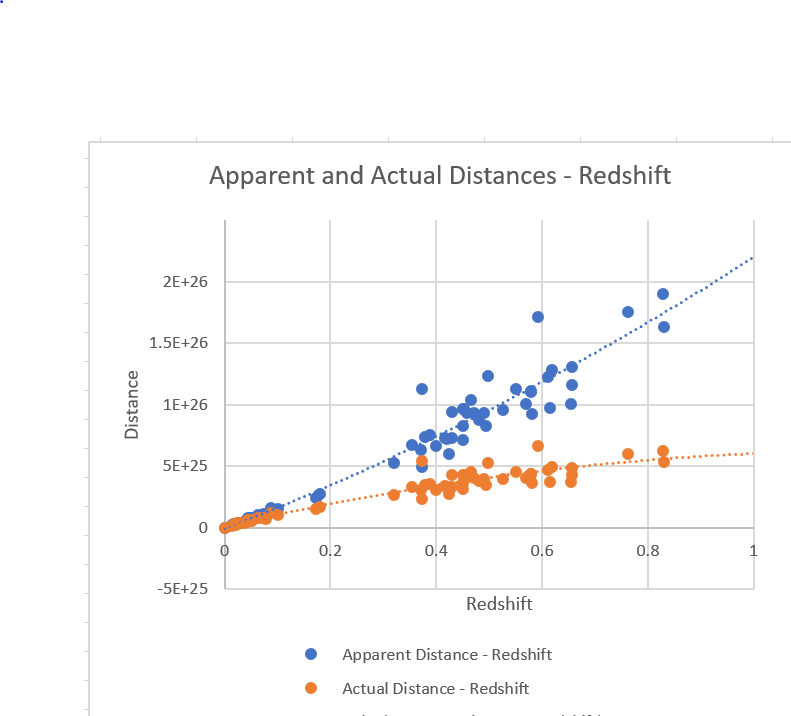
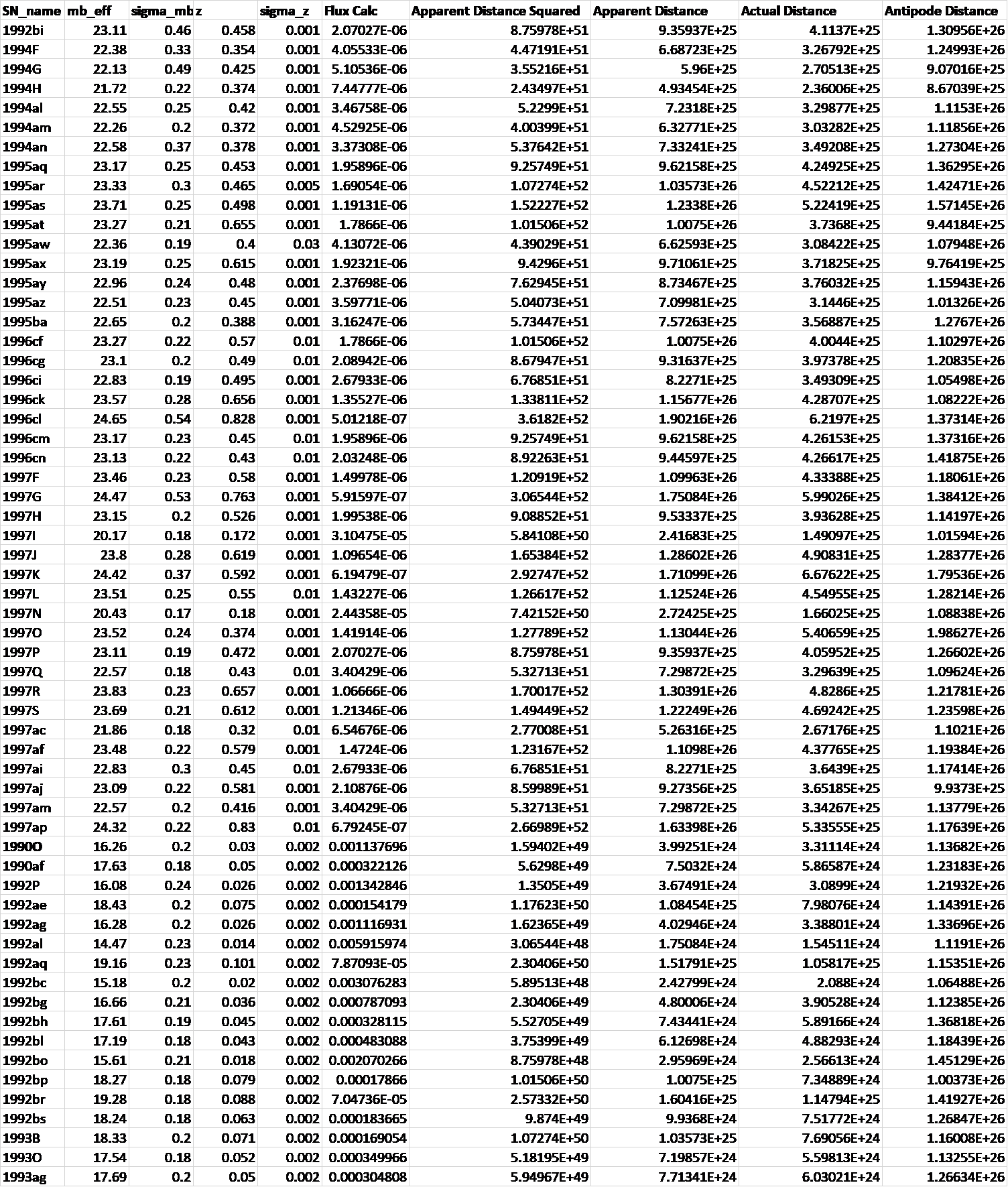
Lensing, Redshift and Distance for Type1A Supernovae.
All data input from Perlmutter et all, https://arxiv.org/pdf/astro-ph/9812133.pdf
The measured Apparent Magnitudes of type 1A Supernovae become converted into fluxes measured in Janskys and these fluxes become converted into Apparent Distances on the basis of the inverse square law taking the Absolute Magnitude of a type 1A supernova as -19.3 at 10 parsecs as the basis of calculation.
The Lensing Equation then gives the Actual Distance for each supernova.
The Redshift-Distance Equation then gives the Antipode distance of the Universe which comes out at ~13 billion light years with only minor divergences, in every case.
The physical principles underlying the Lensing Equation and the Redshift-Distance Equation lie here https://www.specularium.org/hypersphere-cosmology in sections 8 and 5 respectively.
This analysis suggests that the small positive spacetime curvature of a Hyperspherical Universe can account for the apparent discrepancies between observed redshifts and observed apparent magnitudes of type 1A, and the hypotheses of an expanding universe with an accelerating expansion driven by a mysterious ‘dark energy’ become unnecessary.
See also https://www.specularium.org/component/k2/item/390-type-1a-supernovae-part-2